- Home
- About Us
- Scientific Departments
- Laboratories Department
- Environmental Quality Assessment
- Waste Management
- Natural and Technological Hazards
- Numerical Modeling And Geographic Information Systems
- Impact of Built Environment and Nanomaterials
- Engineering For Environmental Protection And Impact Assessment
- Climate Change And Sustainable Development
- Biodiversity And Ecosystem Dynamics Department
- Management Of Natural Resources And Green Energy
- Research activity
- Projects
- Reports
- News
- Contact
Inventarierea instalațiilor de ardere cu o putere termică nominală < 50MW și a motoarelor fixe cu aprindere prin scânteie sau compresie şi evaluarea aportului emisiilor acestora la totalul emisiilor de poluanţi atmosferici
Cunoaşterea cantităţilor de substanţe emise în atmosferă este un reper necesar şi fundamental în elaborarea politicilor de protecţie a mediului şi în monitorizarea unor fenomene, cum ar fi ploile acide, degradarea calităţii aerului, efectul de seră şi schimbările climatice, reducerea stratului de ozon, deteriorarea şi afectarea aspectului clădirilor, expunerea populaţiei şi a ecosistemelor la substanţe periculoase, etc.
Eficiența de ardere scăzută (în special pentru cazanele cu putere instalată sub 1MW), calitatea uneori precară a combustibilului folosit (conţinut ridicat de sulf, putere calorică scăzută, conţinutul ridicat de impurităţi în combustibili, etc) și lipsa sistemelor de reţinere a substanţelor poluante fac ca aceste instalaţii de mică putere să fie considerate a fi surse majore de poluare. Contribuțiile instalațiilor mici de ardere la emisiile totale variază și depind de tipul de poluanți și de zona geografică.
În cadrul proiectului, s-a realizat un dialog interactiv cu deţinătorii de ImA şi motoare staţionare, echipa de elaborare a studiului contribuind semnificativ la procesul de informare-conştientizare a deţinătorilor ImA cu privire la problemele specifice privind evidenţa si raportarea datelor referitoare la caracteristicile tehnice şi datele ce urmează a fi raportate în vederea realizării inventarelor locale de emisii.
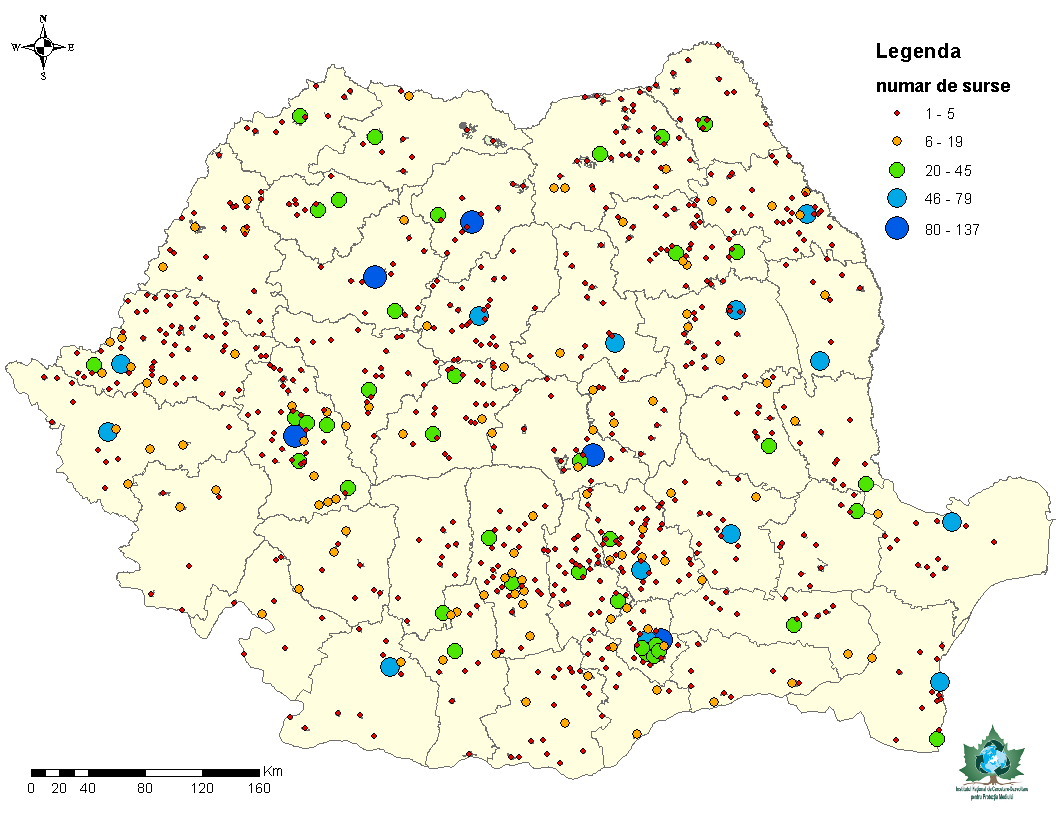
Metodologia de lucru a inclus identificarea surselor de emisii, elaborarea procedurilor necesare obţinerii datelor pentru inventarierea instalatiilor mici de ardere şI motoarelor termice staţionare prin elaborarea chestionarelor în vederea inventarierii ImA, colectarea acestora, verificarea datelor obținute, asigurarea calității datelor, prelucrarea și interpretarea datelor colectate.
- Parteneri
CEPROCIM S.A. - Responsabili de Proiect
Responsabil: Dr. eng. Danut Cociorva, Scientific Researcher II
Responsabil adjunct: Eng. Deák György PhD. habil, Scientific Researcher I
- Perioada de desfășurare
15.03.2013 – 27.05.2013 - Finanțat prin
Ministry of Environment and Climate Change
Objective
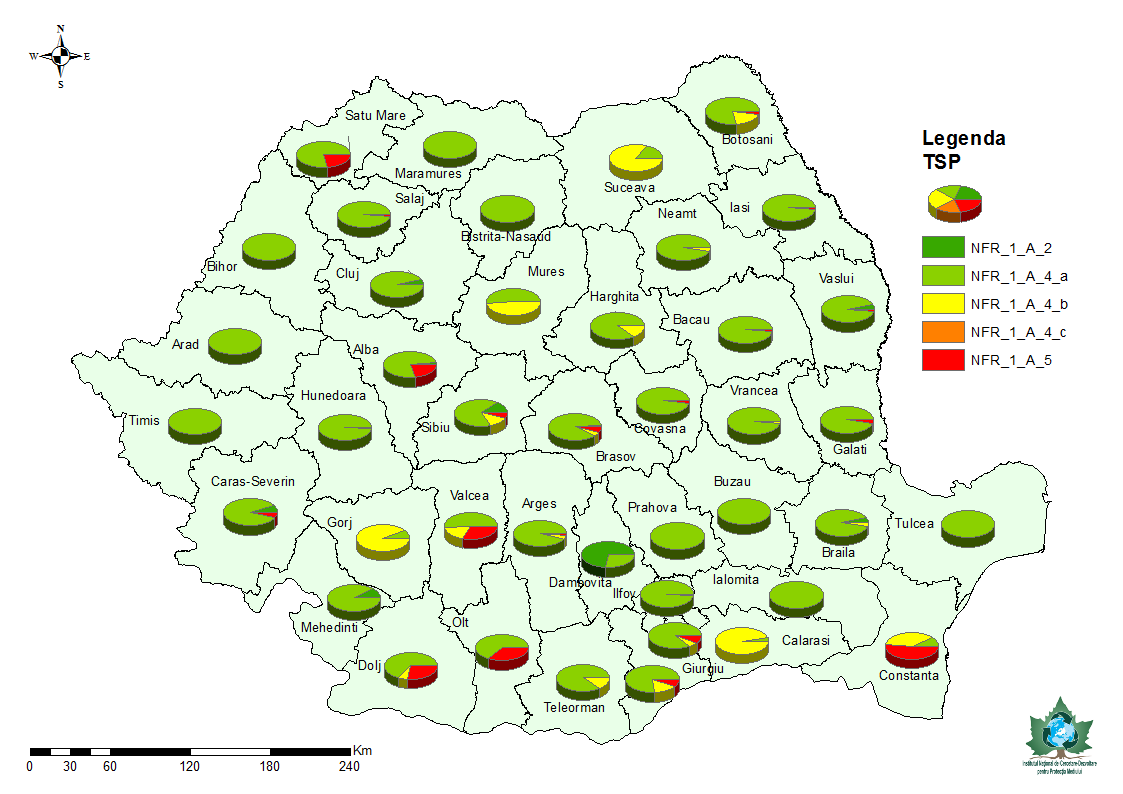
Lucrarea reprezintă o sinteză a activităţilor şi a rezultatelor obţinute în vederea elaborării inventarului instalaţiilor mici de ardere şi a motoarelor staţionare cu putere instalată mai mică de 50MW (activităţile clasificate conform Nomenclatorului pentru Raportare NFR – “Nomenclature for Reporting” la categoria cod NFR 1A4 – Arderi în surse staţionare de mică putere şi la categoria cod NFR 1A2 – Arderi în industrii de fabricare şi construcţii) la nivelul anului 2010.
S-a realizat, deasemenea, şi inventarul emisiilor de poluanţi proveniţi de la instalaţiile mici de ardere şi respectiv de la motoarele staţionare (SO2, NOX, PM10, PM2,5), precum şi evaluarea ponderii acestor emisii la totalul anual al emisiilor naţionale, la nivelul anului 2010.
Rezultate
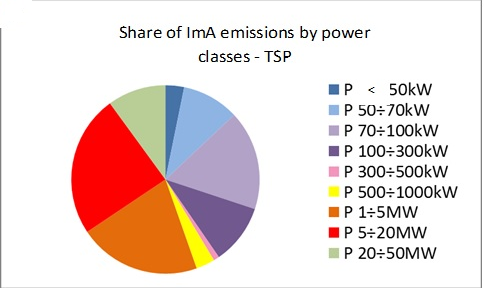
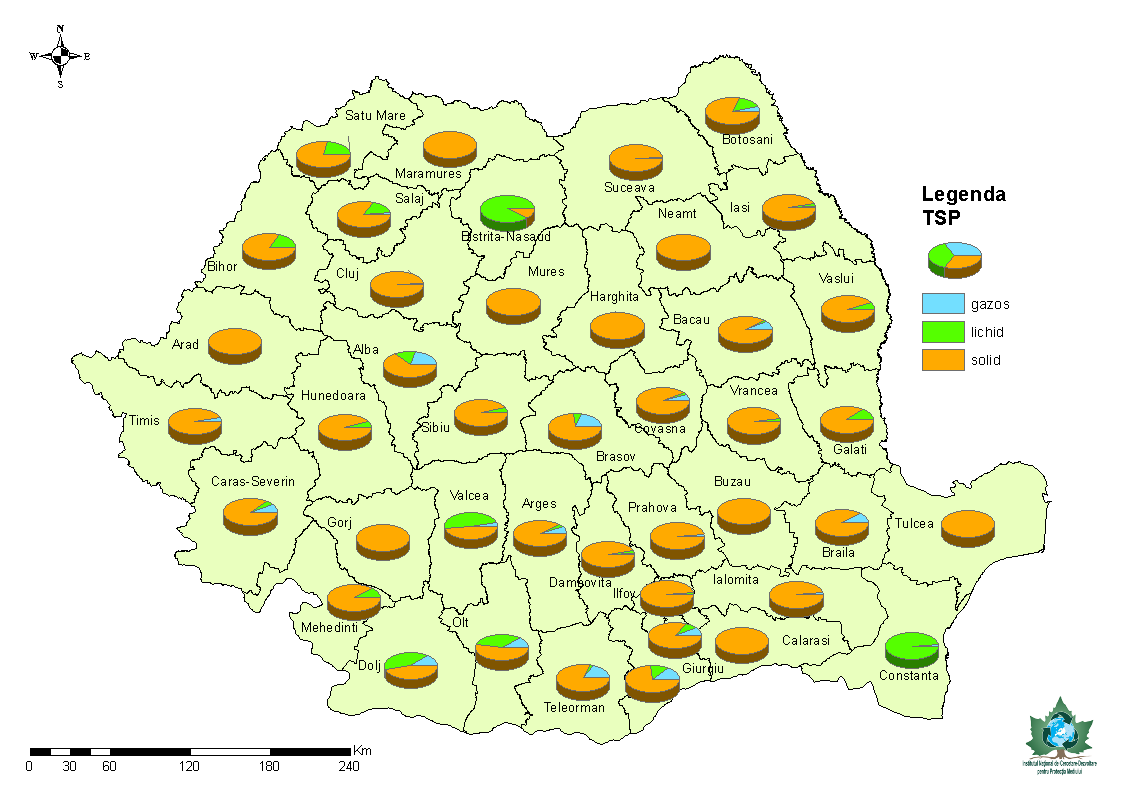
Instalaţiile de ardere pentru încălzirea individuală a locuinţelor şi spaţiilor nerezidenţiale constituie surse de emisie a poluanţilor atmosferici cu contribuţie importantă la emisia naţională de suspensii. Este vorba de suspensiile fine: 98,71% – cu dimensiuni mai mici de 2,5 microni şi 88,15% – cu dimensiuni mai mici de 10 microni (în aprecierea procentelor de participare a ImA la emisia naţională s-a inclus şi emisia motoarelor termice staţionare)
Principalele instalaţii de ardere generatoare de suspensii în atmosferă sunt sobele – 98,89% din emisia totală de pulbri in suspensie şi centralele termice de apartament – 1,11 % din emisia totală de suspensii a instalaţiilor mici de ardere. Combustibilii folisiţi aproape exclusiv în sobe individuale şi centrale termice de apartament sunt lemnele de foc şi gazele naturale: 95,32%, din consumul total de combustibili ai acestor echipamente

Knowing the quantities of substances emitted into the atmosphere is a necessary and fundamental reference in the development of environmental protection policies and in the monitoring of a phenomena such as acid rain, air quality degradation, greenhouse effect and climate change, ozone depletion, deterioration and affecting the appearance of buildings, exposure of the population and ecosystems to hazardous substances, etc.
Low combustion efficiency (especially for boilers with installed power under 1MW), the poor quality of the fuel used (high sulfur content, low calorific power, high content of impurities in fuels, etc.) and lack of pollutant substances restraint systems make that the low-power instalations to be considered the major sources of pollution. Contributions of small combustion plants to total emissions vary and depend on the type of pollutants and the geographical area.
Within the project, an interactive dialogue with ImA holders and stationary engines was carried out, the study team contributing significantly to the information-awareness process of ImA holders on specific issues concerning the recording and reporting of data relating to technical characteristics and the data to be reported for achieving the local emission inventories.
The working methodology included the identification of emission sources, the elaboration of procedures necessary to obtain data for the inventory of small combustion plants and static thermal engines by producing questionnaires for ImA inventory, collection, verification of data obtained, data quality assurance, processing and interpretation of collected data.
- Partners
CEPROCIM S.A. - Project Coordinators
Dr. eng. Danut Cociorva, Scientific Researcher II
Eng. Deák György PhD. habil, Scientific Researcher I
- Period
15.03.2013 – 27.05.2013 - Financed via
Ministry of Environment and Climate Change
Objectives
The paper represent a synthesis of the activities and the results obtained in order to elaborated the inventory of small combustion plants and stationary motors with installed power of less than 50 MW (activities classified according to the NFR Nomenclature for NFR 1A4 code classification – Burnings in small power stationary sources and NFR 1A2 – Burnings in Manufacturing industries and Construction) at the level of 2010.
It has also been achieved, the inventory of pollutant emissions from small combustion plants and respectively from stationary engines (SO2, NOX, PM10, PM2,5), as well as the assessment of the weight of these emissions to the national annual emissions, at the level of of the year 2010.
Results
Combustion installations for individual heating of dwellings and non-residential spaces are sources of emissions of air pollutants with an important contribution to national emission of suspensions. These are the fine suspensions: 98.71% – smaller than 2.5 microns and 88.15% – smaller than 10 microns (the appreciation of the percentages of participation of ImA in the national emission included the emission of thermal motors stationary)
It’s about of fine suspensions: 98.71% – with dimensions smaller than 2.5 microns and 88.15% – with dimensions smaller than 10 microns (in the appreciation of the percentages of participation of ImA in the national emission has been included the emission of the stationary thermal motors ).
The main combustion installations generating suspensions in the atmosphere are the stoves – 98.89% of the total emission of suspended powders and the apartment’s thermal plants – 1.11% of the total emission of the small combustion plant suspensions. Fuels used almost exclusively in individual stoves and apartment heating boilers are firewood and natural gases: 95.32%, of the total fuel consumption of these equipments.
It’s about of fine suspensions: 98.71% – with dimensions smaller than 2.5 microns and 88.15% – with dimensions smaller than 10 microns (in the appreciation of the percentages of participation of ImA in the national emission has been included the emission of the stationary thermal motors ).
The main combustion installations generating suspensions in the atmosphere are the stoves – 98.89% of the total emission of suspended powders and the apartment’s thermal plants – 1.11% of the total emission of the small combustion plant suspensions. Fuels used almost exclusively in individual stoves and apartment heating boilers are firewood and natural gases: 95.32%, of the total fuel consumption of these equipments.